2021 Investment Climate Statements: Latvia
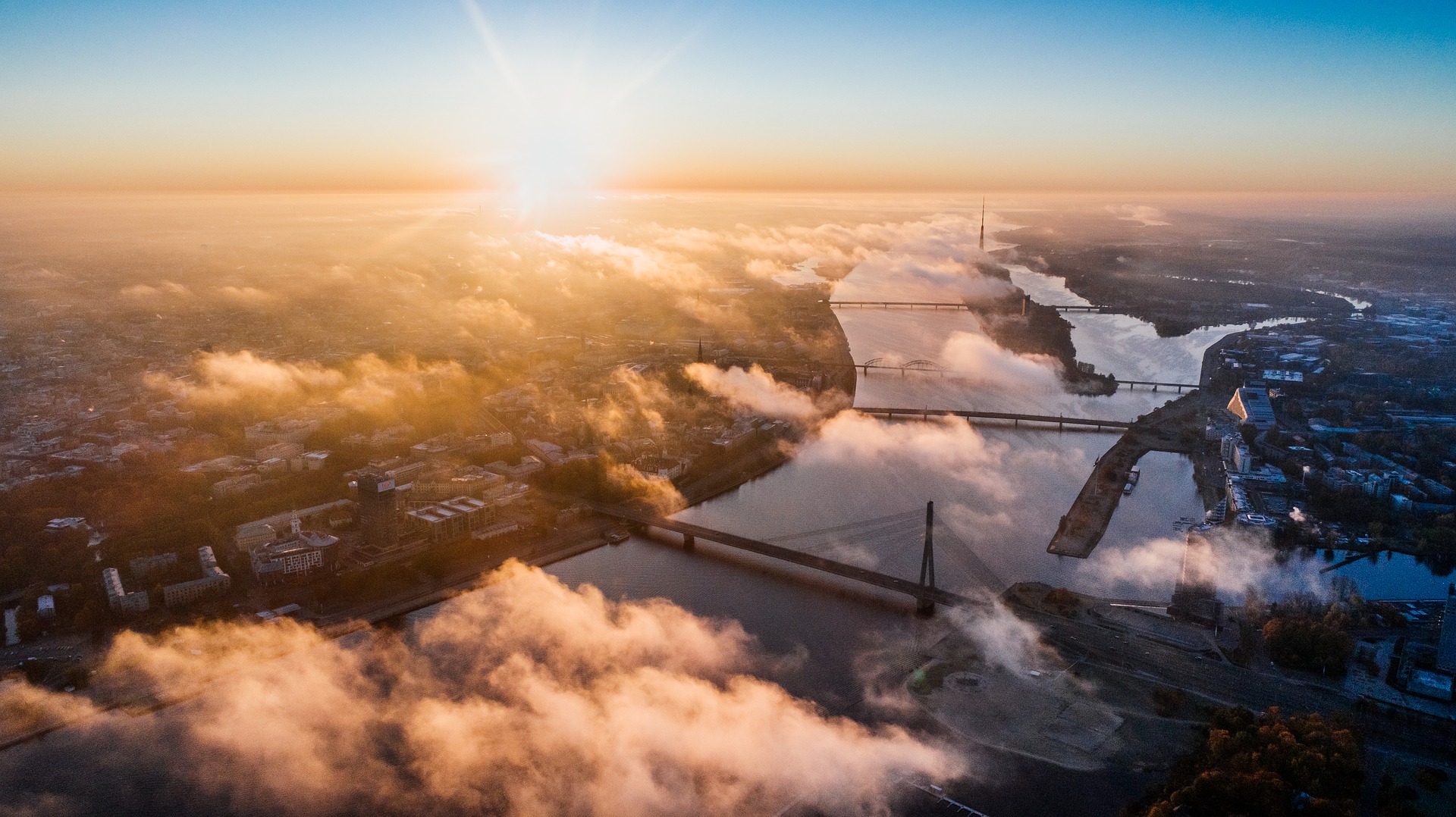
Located in the Baltic region of northeastern Europe, Latvia is a member of the EU, Eurozone, NATO, OECD, and the World Trade Organization (WTO). The Latvian government recognizes that, as a small country, it must attract foreign investment to foster economic growth, and thus has pursued liberal economic policies and developed infrastructure to position itself as a transportation and logistics hub. According to the 2020 World Bank’s Doing Business Report, Latvia is ranked 19th out of 190 countries in terms of ease of doing business, which is the same as the previous year. As a member of the European Union, Latvia applies EU laws and regulations, and, according to current legislation, foreign investors possess the same rights and obligations as local investors (with certain exceptions). Any foreign investor is entitled to establish and own a company in Latvia and has the opportunity to acquire a temporary residence permit.
Latvia provides several advantages to potential investors, including:
Regional hub: Despite ongoing tensions between Russia and the European Union and challenges of Covid-19 pandemic, Latvia remains a transportation and logistics bridge between West and East, providing strategic access to both the EU market and to Russia and Central Asia. Latvia’s three ice-free ports are connected to the country’s rail and road networks and to the largest international airport in the Baltic region (Riga International Airport). Latvia’s road network is connected to both European and Central Asian road networks. The railroads connect Latvia with the other Baltic States, Russia, and Belarus, with further connections extending into Central Asia and China.
Workforce: Latvia’s workforce is highly educated and multilingual, and its culture promotes hard work and dependability. Labor costs in Latvia are the fourth lowest (tied with Hungary) in the EU.
Competitive tax system: Latvia ranked second in the OECD’s 2020 International Tax Competitiveness Index Rankings. To further boost its competitiveness, the Latvian government has abolished taxes on reinvested profits and has established special incentives for foreign and domestic investment. There are five special economic zones (SEZs) in Latvia: Riga Free Port, Ventspils Free Port, Liepaja Special Economic Zone, Rezekne Special Economic Zone, and Latgale Special Economic Zone, which provide various tax benefits for investors. The Latgale Special Economic Zone covers a large part of Latgale, which is the most economically challenged region in Latvia, bordering Russia and Belarus.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Latvia’s GDP contracted by 3.6 percent in 2020. However, this contraction was less severe than what most other Eurozone countries experienced during the crisis.
According to the government, growth in manufacturing and construction and increased government spending helped offset the decline in services caused by COVID-19-related restrictions in transport, tourism, and entertainment and leisure industries. The most competitive sectors in Latvia remain woodworking, metalworking, transportation, IT, green tech, healthcare, life science, food processing, and finance. Recent reports suggest that some of the most significant challenges investors encounter in Latvia are a shortage of available workforce, demography, quality of education, and a significant shadow economy.
The non-resident banking sector has come under increased regulatory scrutiny in recent years because of inadequate compliance with international AML standards. On August 23, 2018, MONEYVAL, a Council of Europe agency that assesses member states’ compliance with AML standards, issued a report that found Latvia deficient in several assessment categories. The Government of Latvia has continued its work to restore confidence in its financial institutions and has passed several pieces of reform legislation.
In late 2019 and early 2020, MONEYVAL and the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) concluded that Latvia had developed and implemented strong enough reforms for combating financial crimes to avoid increased monitoring via the so-called “grey list.” While it will continue enhanced monitoring under MONEYVAL to continue strengthening the system, Latvia became the first member state under the MONEYVAL review to successfully implement all 40 FATF recommendations.
Despite these advantages, some investors note a perceived lack of fairness and transparency with Latvian public procurements. Several companies, including foreign companies, have complained that bidding requirements are sometimes written with the assistance of potential contractors or couched in terms that exclude all but “preferred” contractors.
 Facebook
Facebook