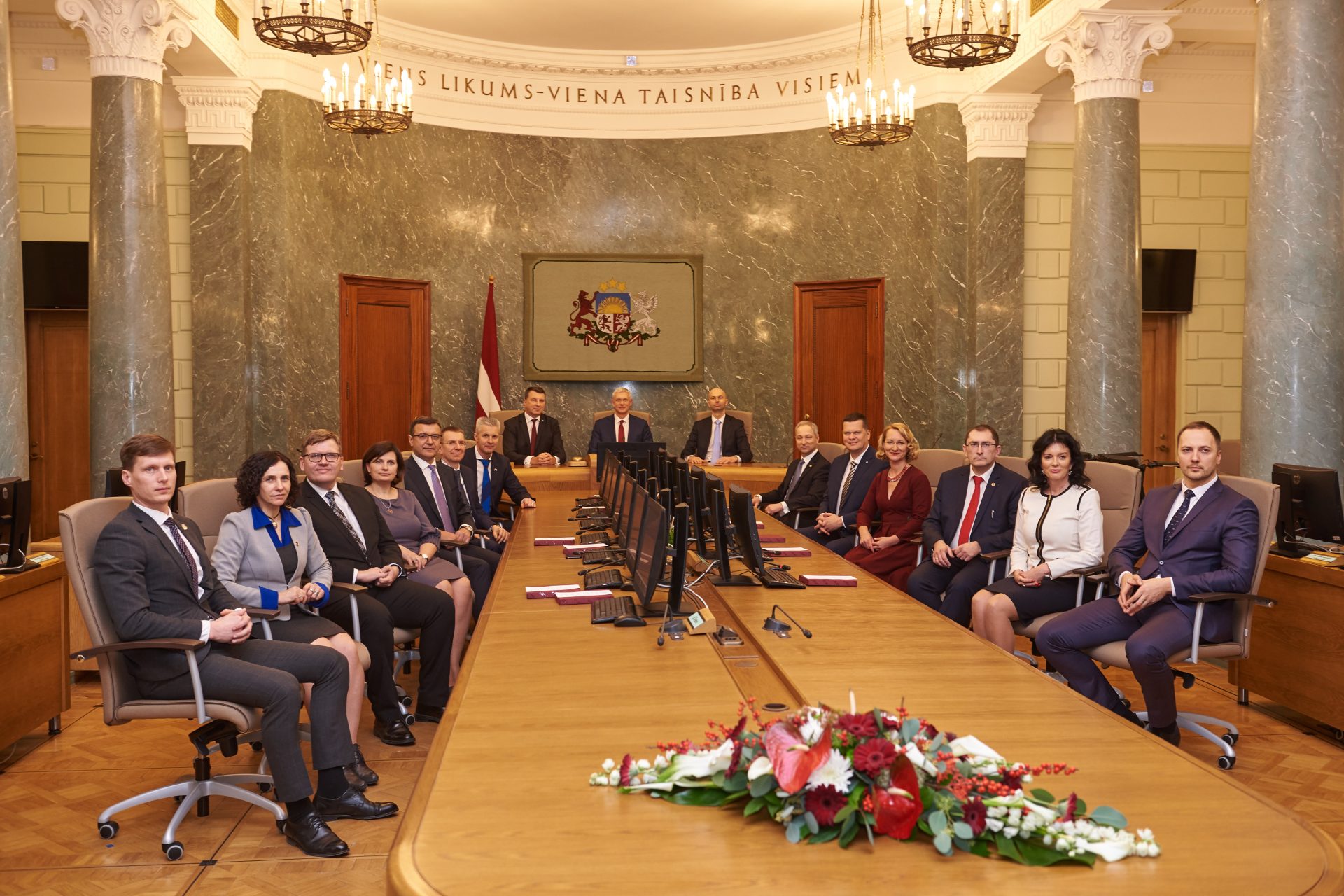
Latvia’s new Prime Minister announces his Cabinet
On Wednesday, 23 January, during its extraordinary sitting, the Saeima gave a vote of confidence to the new Cabinet of Ministers headed by Prime Minister Krišjānis Kariņš.
Addressing the Cabinet of Ministers headed by K. Kariņš, President Raimonds Vējonis underscored: “In order to increase the public confidence in politicians and the political processes in the country as a whole, the government will have to act fast and decisively. The residents of Latvia expect that from the very first day each and every one of you will take the responsibility for your country not only in words, but also in deeds. Each of you individually and, most importantly, all of you together are now responsible for the policy implemented by the government.”
In the first formal sitting of the government Prime Minister K. Kariņš addressed the ministers by emphasizing: “We will work together, listen to and support each other in order to implement the three main objectives of this government – increase the well-being of the nation, ensure fairness and justice, and reduce the inequality in all its aspects in the society. We will do it.”
The government headed by K. Kariņš will be composed of Deputy Prime Minister and Minister for Defence Artis Pabriks, Deputy Prime Minister and Minister for Justice Jānis Bordans, Minister for Foreign Affairs Edgars Rinkēvičs, Minister for Economics Ralfs Nemiro, Minister for Finance Jānis Reirs, Minister for the Interior Sandis Ģirģens, Minister for Education and Science Ilga Šuplinska, Minister for Culture Dace Melbarde, Minister for Welfare Ramona Petraviča, Minister for Transport Tālis Linkaits, Minister for Health Ilze Vinķele, Minister for Environmental Protection and Regional Development Juris Pūce and Minister for Agriculture Kaspars Gerhards.
According to the Declaration, the government of K. Kariņš will primarily focus on the alignment of the financial system, the strengthening of the national security and the rule of law, the implementation of the administrative-territorial reform, the improvement of the quality and accessibility of the health care system and the education system. The government will also address the removal of the mandatory procurement component, the increase of the economic competitiveness, productivity and investment, and the improvement of the demographic situation. The work on the implementation of these priorities will be based on a strict fiscal discipline with the intention of building surpluses in the state budget.
 Facebook
Facebook